
By Darren Robinson | Aug 22, 2024
8 minute read Blog| Technology| Cybersecurity
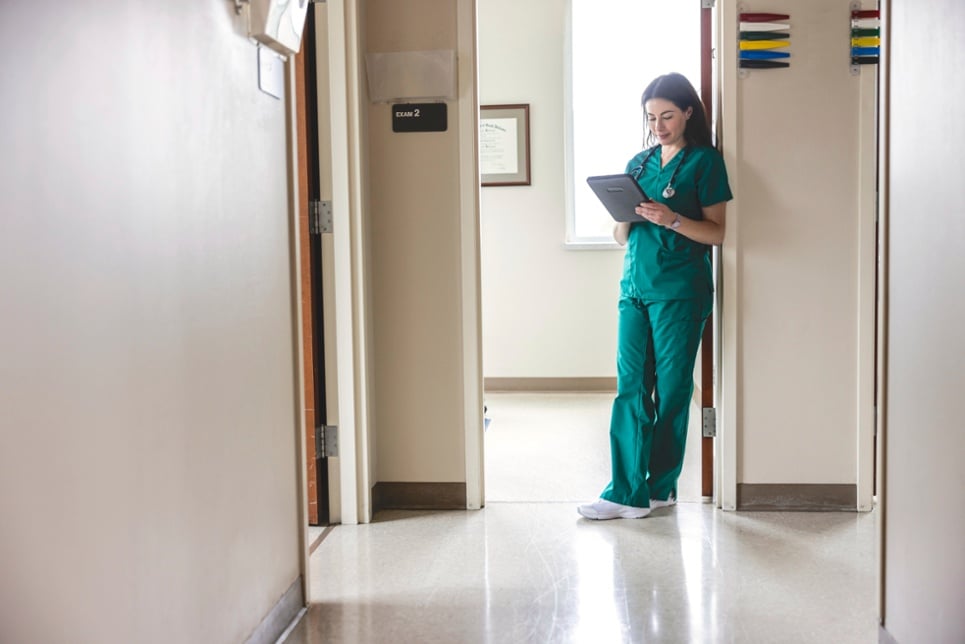
In today’s digital age, the healthcare industry is more connected than ever, leveraging technology to enhance patient care, streamline operations, and improve outcomes. However, this increased reliance on digital systems also brings significant cybersecurity challenges. Healthcare organisations are prime targets for cybercriminals, as healthcare data is a lucrative asset due to its sensitive and valuable nature. A successful cyberattack can lead to devastating consequences, including data breaches, operational disruptions, financial loss, and even threats to patient safety.
As cyber threats evolve in sophistication and frequency, healthcare providers must stay ahead by adopting robust cybersecurity measures. This blog will explore the most pressing cybersecurity risks faced by the healthcare industry today and propose effective solutions and strategies to mitigate these risks.
The healthcare industry is facing an unprecedented wave of cybersecurity threats. As digital transformation continues to reshape healthcare, with electronic patient records (EPRs), telemedicine, and connected medical devices becoming commonplace, the attack surface for cybercriminals has expanded significantly. Unfortunately, this digital evolution has also made healthcare a prime target for malicious actors seeking to exploit vulnerabilities for financial gain or to cause widespread disruption.
Cyberattacks against healthcare organisations[1] have been increasing in both frequency and complexity. Recent studies[2] indicate that the healthcare sector suffers from some of the highest numbers of data breaches compared to other industries. These breaches often involve highly sensitive patient information, making them particularly damaging. In addition to data theft, healthcare organisations face the threat of ransomware, where attackers encrypt critical data and systems, demanding a substantial ransom for their release.
Healthcare organisations are uniquely attractive to cybercriminals for several reasons. One reason is that personal data stored within healthcare systems is highly valuable on the black market. Patient records contain medical histories and other personal identifiers, making them a goldmine for identity theft and fraud. Additionally, healthcare organisations often operate with legacy systems and outdated software, which can have unpatched vulnerabilities that are easier for attackers to exploit.
Moreover, the healthcare industry’s focus on patient care often means that cybersecurity may not be as prioritised as in other sectors. This can lead to a suboptimal cybersecurity posture, making it easier for attackers to infiltrate systems. The critical nature of healthcare services also means that organisations may be more willing to pay ransoms to restore operations quickly, further incentivising ransomware attacks.
The impact of a cybersecurity breach in healthcare can be devastating. Beyond the financial costs of fines, legal fees, and ransom payments, the repercussions can include significant operational disruptions. When systems are compromised, healthcare providers may be forced to revert to manual processes, delaying patient care and potentially endangering lives. Furthermore, breaches can severely damage an organisation’s reputation, losing trust among patients and partners.
Of most concern is the potential impact on patient safety. Cyberattacks that target critical systems, such as those controlling medical devices or storing patient data, can have direct and life-threatening consequences. The stakes are higher in healthcare than in many other industries, making the need for robust cybersecurity measures even more urgent.
The healthcare industry faces various cybersecurity risks, each potentially causing significant harm to organisations and patients. With healthcare digitisation, understanding these risks is crucial for developing effective mitigation strategies. Below are some of the most prevalent cybersecurity threats facing the healthcare sector today.
Phishing remains a leading method used by cybercriminals to infiltrate healthcare systems. In these attacks, deceptive emails or messages, often disguised as communications from trusted sources, trick recipients into revealing sensitive information or downloading malware. The fast-paced, high-pressure environment in healthcare settings can lead employees to inadvertently click on malicious links or share confidential data, resulting in data breaches or system compromises.
Social engineering tactics, where attackers manipulate individuals into divulging confidential information, are also a significant threat. These attacks often target staff with access to critical systems, exploiting human error rather than technical vulnerabilities.
Ransomware is a particularly destructive form of malware that encrypts an organisation’s data, making it inaccessible until a ransom is paid. The healthcare industry has seen a sharp rise in ransomware attacks, with hospitals and clinics often forced to choose between paying the ransom or losing critical patient data and facing operational shutdowns. The urgency in healthcare settings makes these organisations prime targets, as the potential impact on patient care can pressure organisations into paying ransoms quickly.
Ransomware attacks disrupt healthcare services, delay treatments, compromise patient safety, and erode trust among patients and partners.
As healthcare organisations increasingly expose services like patient portals and telehealth platforms to the Internet, they become more vulnerable to Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks. In a DDoS attack, cybercriminals overwhelm a service with traffic, rendering it unavailable to legitimate users. For healthcare providers, this can mean patients cannot access vital services, such as booking appointments or viewing test results, leading to frustration, delays in care, and potential damage to the organisation’s reputation.
DDoS attacks can also serve as a smokescreen for more sophisticated cyberattacks, diverting attention while attackers exploit other vulnerabilities within the system.
Many healthcare organisations rely on legacy systems—outdated hardware and software that vendors no longer support. These systems often lack the security features needed to defend against modern cyber threats and may have unpatched vulnerabilities that are easy targets for attackers. However, the cost and complexity of upgrading or replacing these systems can be prohibitive, leaving healthcare providers stuck with insecure technology.
Using legacy systems poses a significant risk, as they can be exploited to gain access to sensitive data or disrupt critical operations, leading to data breaches, compliance failures, and compromised patient care.
Healthcare organisations often work with many third parties, including partners, vendors, and suppliers, to deliver comprehensive care. While these relationships are essential, they also introduce significant cybersecurity risks. Third parties may have access to sensitive information or critical systems; if their security measures are inadequate, they can serve as a gateway for attackers.
Managing third-party risks requires healthcare organisations to carefully vet their partners’ security practices, monitor ongoing compliance, and establish clear data sharing and access control protocols.
The proliferation of connected medical devices, often called the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT), has introduced new vulnerabilities into healthcare environments. Many of these devices, including insulin pumps and imaging systems, are connected to hospital networks and can be targeted by cybercriminals. These devices often run on outdated software and lack robust security features, making them susceptible to hacking.
A compromised medical device can have dire consequences, including manipulating its function, which can put patients’ lives at risk.
The increasing mobility of healthcare professionals has expanded the attack surface for cybercriminals. Mobile devices and remote access to healthcare systems are commonplace but also introduce significant security risks. These devices may be lost or stolen or be connected to unsecured networks, exposing sensitive data to potential breaches.
Moreover, using personal devices in the workplace, known as Bring Your Own Device (BYOD), complicates the enforcement of security policies. Ensuring the security of mobile and remote workforces requires strong encryption, secure access protocols, and comprehensive mobile device management (MDM) solutions.
Data breaches remain a significant concern in healthcare, where protecting sensitive patient information is paramount. A data breach occurs when an unauthorised party gains access to confidential information, which can be used for identity theft, financial fraud, or other malicious purposes. Healthcare data breaches are particularly damaging because they often involve extensive personal and medical information, which is difficult to change or replace, unlike financial data.
These breaches can occur through various means, including hacking, physical theft of devices, or even improper disposal of records. However, one of the most concerning trends is the rising impact of insider threats. According to the Verizon 2024 Data Breach Investigations Report[1], the healthcare sector has seen increased malicious insider activity. Insiders, whether through deliberate misuse of privileges or unintentional errors, are now a leading cause of data breaches in healthcare.
The consequences of a data breach can be severe, leading to regulatory fines, legal action, and a significant loss of trust among patients and partners. Given the potential for insiders to cause considerable harm, healthcare organisations must prioritise monitoring and controlling internal access to sensitive data as part of their broader cybersecurity strategy.
As healthcare organisations navigate an increasingly complex and evolving threat landscape, implementing robust cybersecurity strategies is essential to safeguarding sensitive data, ensuring operational continuity, and maintaining patient trust. Below are strategies healthcare organisations can adopt to enhance their cybersecurity posture.
Challenge: You cannot secure what you do not understand. Many healthcare organisations need more visibility into their existing IT environment, which can leave critical assets and vulnerabilities unidentified.
Solution: A thorough understanding of your organisation’s networks, systems, and assets is the first step towards effective cybersecurity. CereCore International helps healthcare providers develop situational awareness by:
Healthcare organisations can better prioritise security efforts and protect critical assets by establishing situational awareness.
Challenge: Identifying and prioritising vulnerabilities across the organisation’s digital environment can be daunting.
Solution: Regular and thorough risk assessments are crucial for understanding where potential threats lie. CereCore International offers expert advisory services to help healthcare organisations conduct comprehensive risk assessments. We assist in evaluating vulnerabilities within networks, applications, devices, and third-party vendors, providing actionable plans to mitigate identified risks. Regular reviews ensure that strategies remain effective as new threats emerge.
Challenge: Advanced and evolving threats require sophisticated technologies for effective detection and prevention.
Solution: Healthcare organisations must invest in cutting-edge security technologies to combat sophisticated cyber threats. CereCore International can advise on critical technologies to improve an organisation’s security posture.
Challenge: Human error remains a leading cause of cybersecurity incidents.
Solution: Regular security awareness and training are critical to reducing the risk of human error. CereCore International offers tailored training programmes that cover key areas such as phishing prevention, secure handling of patient data, and compliance with security protocols. Additionally, we conduct simulated phishing attacks and tabletop exercises to reinforce lessons and ensure staff are prepared to handle potential threats effectively.
Challenge: Uncontrolled or poorly managed access to systems and data can lead to significant security breaches, particularly if malicious actors access privileged accounts.
Solution: Strengthening Identity and Access Management (IAM) ensures that only authorised individuals can access sensitive systems and data within a healthcare organisation. CereCore International offers comprehensive IAM solutions that include:
Challenge: Connected medical devices introduce new vulnerabilities into healthcare environments.
Solution: Securing these devices is critical as the IoMT continues to grow. CereCore International helps healthcare organisations:
Challenge: Slow or disjointed responses to cyber incidents can exacerbate damage and prolong recovery.
Solution: A well-defined incident response plan (IRP) is essential for managing and mitigating the impact of cybersecurity incidents. CereCore International help healthcare organisations develop detailed IRPs, conduct tabletop exercises to prepare teams, and ensure cross-department coordination for swift, effective responses.
Challenge: Cyber threats constantly evolve, requiring continuous updates to security policies.
Solution: Updating security policies is essential for protecting against new and emerging threats. CereCore International supports healthcare organisations by regularly reviewing and updating security policies, revising access controls, and ensuring staff adherence to the latest protocols. We also provide strategic advisory services to help organisations stay informed about the latest cybersecurity trends and adapt their strategies accordingly.
Challenge: Financial constraints can limit the ability to invest in comprehensive cybersecurity measures.
Solution: CereCore International offers strategic advisory services to help healthcare organisations optimise their cybersecurity investments. We work closely with clients to prioritise spending based on organisational goals and risk management needs, ensuring that limited resources are used effectively to bolster security and enhance overall cybersecurity posture.
Cybersecurity is essential for protecting healthcare organisations against evolving cyber threats. By prioritising robust cybersecurity measures, healthcare providers can maintain patient trust, operational continuity, and regulatory compliance.
At CereCore International, we understand the unique cybersecurity challenges faced by the healthcare industry. Our expert team is dedicated to helping healthcare organisations strengthen their cyber defences through tailored advisory services. By partnering with CereCore International, healthcare organisations can implement these cybersecurity strategies more effectively, reducing their risk of cyber incidents, protecting sensitive data, and ensuring the continuity of critical healthcare services. Our comprehensive approach addresses both technological and human factors, creating a multi-layered defence against the increasingly complex array of cyber threats facing the healthcare sector.
Please visit our Cybersecurity Advisory Services page for a personalised consultation and to explore how CereCore International can help strengthen your cybersecurity strategy.
Let us help you protect your organisation and secure patient data against the ever-evolving threat landscape.
[1] Verizon 2023 Data Breach Investigations Report
[1] Recent examples include Synnovis and the University of Manchester.
Director, Technology and Cloud at CereCore International
Director, Technology and Cloud at CereCore International
What happens when bold leadership meets groundbreaking technology?
Mater Private Network is one of Ireland’s leading private healthcare providers, known for delivering world-class services in medical and surgical care.
Despite the Federated Data Platform being an NHS England priority for years, it still feels like a solution in search of a problem. Not because the NHS is short on problems – if only – but because...
Let us know how we can support your initiatives and take some of the heavy lifting from healthcare IT.

© All Rights Reserved CereCore Terms of Service Notice at Collection Privacy Policy Do Not Sell My Personal Information Responsible Disclosure